What is Candida Auris, and why is it so dangerous
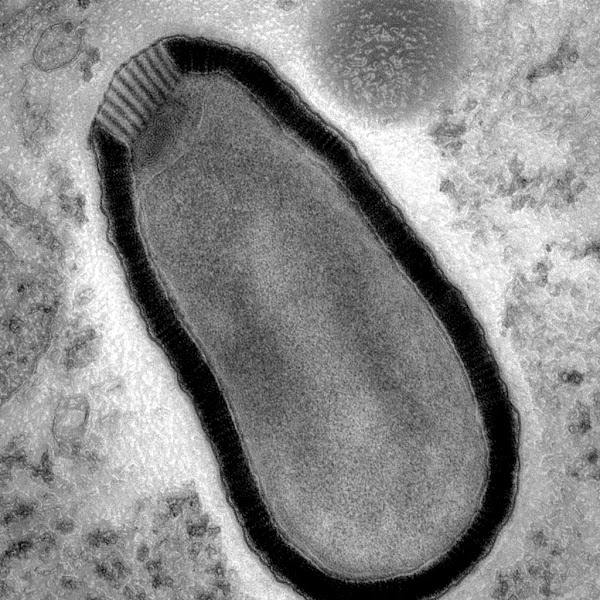
Candida auris is a type of yeast that can cause severe infections in humans. It was first identified in 2009 in Japan and has since been found in many other countries, including the United States, India, and several European countries.
Candida auris infections are particularly concerning because this yeast is often resistant to multiple types of antifungal medications. This can make it difficult to treat and control infections, especially in healthcare settings where patients may already be vulnerable to infections. In addition, C. auris is capable of surviving on surfaces for long periods of time, which can contribute to its spread.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) considers Candida auris to be an emerging global threat to public health, and it has been classified as a serious threat by the World Health Organization (WHO).
What type of fungus is Candida Auris?
Candida auris is a type of fungus that belongs to the Candida genus, which includes many species of yeast. This fungus is a member of the same group of fungi that cause common infections like thrush and vaginal yeast infections. However, Candida auris is different in several important ways. Auris is the Latin word for ear. Despite its name, C. auris can also affect many other regions of the body and can cause invasive infections, including bloodstream infections and wound infections.
Firstly, it is often resistant to multiple types of antifungal medications, making it difficult to treat. This is partly due to its ability to form biofilms, which are clusters of microorganisms that can protect against drugs and immune responses. Additionally, C. auris has a high rate of genetic mutations, which allows it to rapidly adapt to new environments and develop resistance to drugs.
Candida auris is also concerning because it is capable of surviving on surfaces for extended periods of time, which can lead to outbreaks in healthcare facilities. It has been found on a variety of surfaces, including hospital equipment and furniture, and it can spread easily from person to person.
It is important to note that Candida auris is relatively rare, and most people who come into contact with it do not develop an infection. However, for those who do, it can be a serious and sometimes fatal condition, particularly if it is not treated promptly and effectively.
Who is most at risk
People who are most at risk of developing a Candida auris infection include those who have weakened immune systems, particularly those who are hospitalized or living in long-term care facilities. This includes people who have recently undergone surgery, received broad-spectrum antibiotics or other immunosuppressive medications, or have medical devices such as feeding tubes or catheters.
In addition, people who have previously had a Candida auris infection or who have had frequent contact with healthcare facilities may also be at increased risk. This includes healthcare workers, family members of patients, and visitors to healthcare facilities.
What treatments exist for Candida auris
Candida auris infections can be challenging to treat because this yeast is often resistant to multiple types of antifungal medications. However, several treatments are available that may be effective in some cases.
The specific treatment for Candida auris infections will depend on several factors, including the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health. In general, treatment may involve the use of antifungal medications such as echinocandins, azoles, or amphotericin B. However, the choice of medication will depend on the results of laboratory testing to determine the susceptibility of the specific strain of Candida auris to different drugs.
It's worth noting that some Candida auris strains may be resistant to all available antifungal medications, making treatment extremely challenging. In such cases, supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications may be the only option.
Prevention is also an important strategy for managing Candida auris infections. This includes measures such as good hand hygiene, using contact precautions in healthcare settings, and promptly identifying and isolating infected patients.
Is Candida auris fatal
Yes, Candida auris infections can be fatal, especially in people who are already ill or have weakened immune systems. The mortality rate of Candida auris infections varies depending on factors such as the patient's age, overall health, and the severity of the infection.
Candida auris infections are concerning because they are often resistant to multiple types of antifungal medications, making them more difficult to treat. In addition, C. auris infections can sometimes lead to complications such as sepsis, which is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body's response to an infection causes damage to its own tissues and organs.
For more information on this Desease please visit CDC publication on Candida auris.